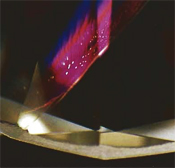
Detecting Clarity
Enanced Diamonds: "The Flash Effect"
The
clarity enhancement process has its own signature
on treated diamonds. This known as the "Flash
Effect". It is the built-in signature of any
CE diamond and the easiest way to detect CE.
To find it,
hold the diamond with a pair of tweezers by its
girdle, under a 10x loupe with dark field or direct
lighting, or under a high-power gem microscope.
Tilt the diamond carefully back and forth and look
perpendicular to the surface. Certain distinct subtle
colors are seen. One should look for a flash with
a purple, blue, violet-pink or yellow-orange colors.
Other
Diamond Enhancements
Diamond
enhancement relates to the sophisticated process that
alters the appearance of a diamond, such as lasered,
fracture filled, or irradiated.
Lasered
Diamond
Lasered
diamond is one that has been laser drilled into
the diamond to a dark inclusions. This is a sophisticated
method that to remove the dark substance (diamond
graphite). "Soaking" or "Deep Boiling"
needs to be applied in order to totally remove those
dark inclusions. This leaves a white inclusion and
a very small (microscopic) hole. The drill is a
permanent change to the diamond, however it is accepted
today within the trade and it is the only enhancement
that most labs will certify.
Irradiated
Diamond
Irradiation
is a process in which a diamond is exposed to high
amounts of radiation, which artificially alters or
improves the color of the diamond. Once color treated
with radiation the diamond alters its color and can
appear blue or green. This is much less expensive
then a natural dark colored diamond.
Synthetic
and Simulated Diamonds
A
synthetic gemstone is one that has the entire chemical
and physical properties of its natural counterpart
diamond, however those properties are man made in
a laboratory environment. A simulant is a different
gem that is cut to look like a diamond and is used
as a diamond substitute.
There are many
stones that are cut to look like diamonds. The big
scare back in the 1960's was fabulite, in the 70's
it was cubic zirconia, but today we can all pick
out these materials as non-diamonds with relative
ease. Today there is a new material coming out on
the market it is called synthetic moissanite.
It
is the hardest gem next to diamond. On the Mohs scale
synthetic moissanite is rated 9.25 and a diamond is
a 10. This is actually a big difference. Synthetic
moissanite is not hard enough to polish sharp facet
junctions as on a diamond. Moissanite, in its natural
form, is usually too small to be cut into gemstones
and is very dark in color usually dark green. The
labs that grow synthetic moissanite have been able
to lighten the color to be closer to the near colorless
range and faceted to look much like a shallow cut
diamond. Some other diamond simulants are White Sapphire,
GGG, White Zircon, and Glass.
Some
signs and tales that indicate a non-diamond stone.
-
The
girdle is not smooth it looks pitted and rough.
-
The
inclusions are brown instead of black
-
The
inclusions look unusual.
-
The
stone doesn't "sparkle" like a diamond.
-
|
|


Laser Drilling
Source: GIA Research
Source: GIA Research
|
